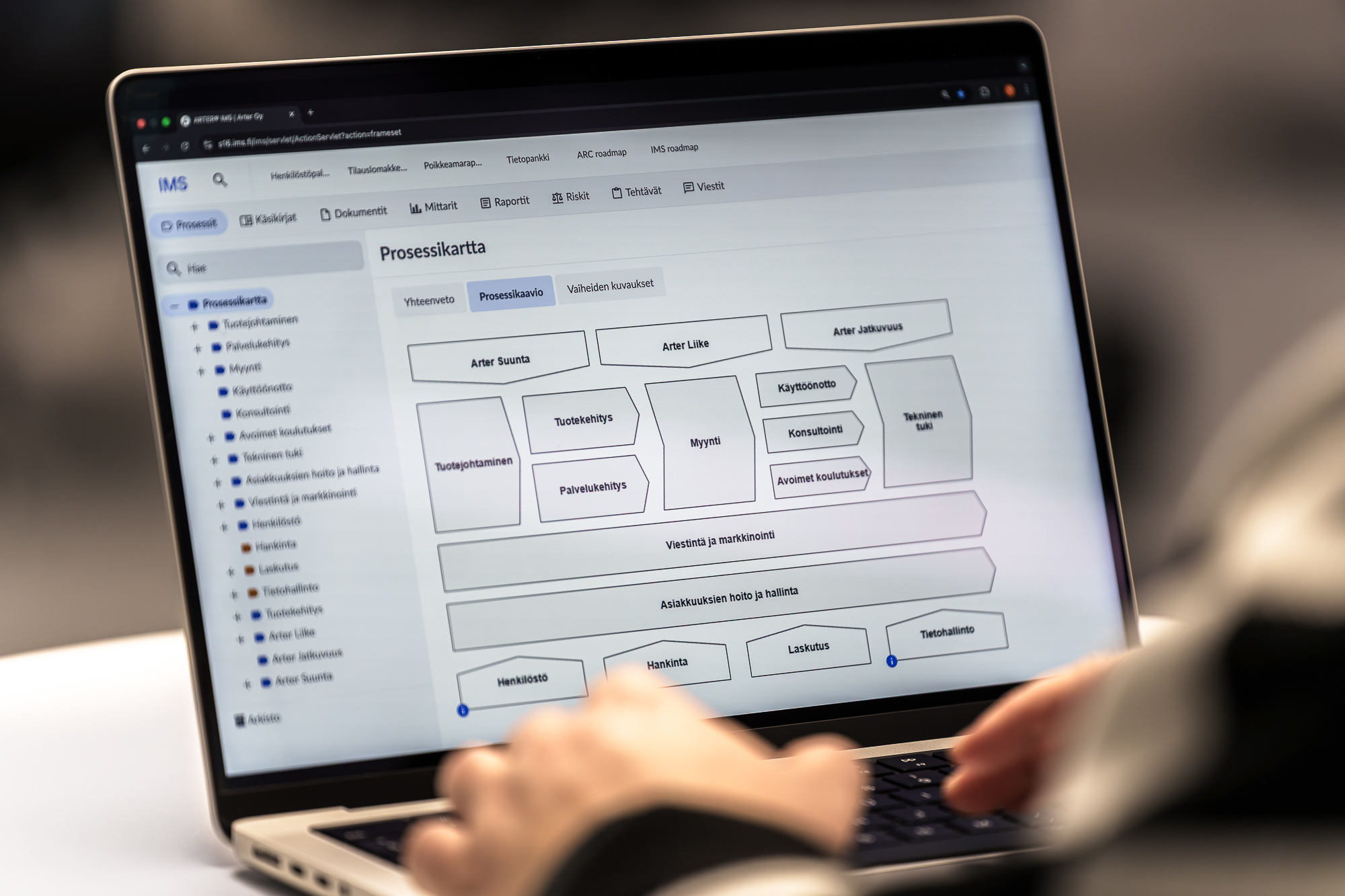
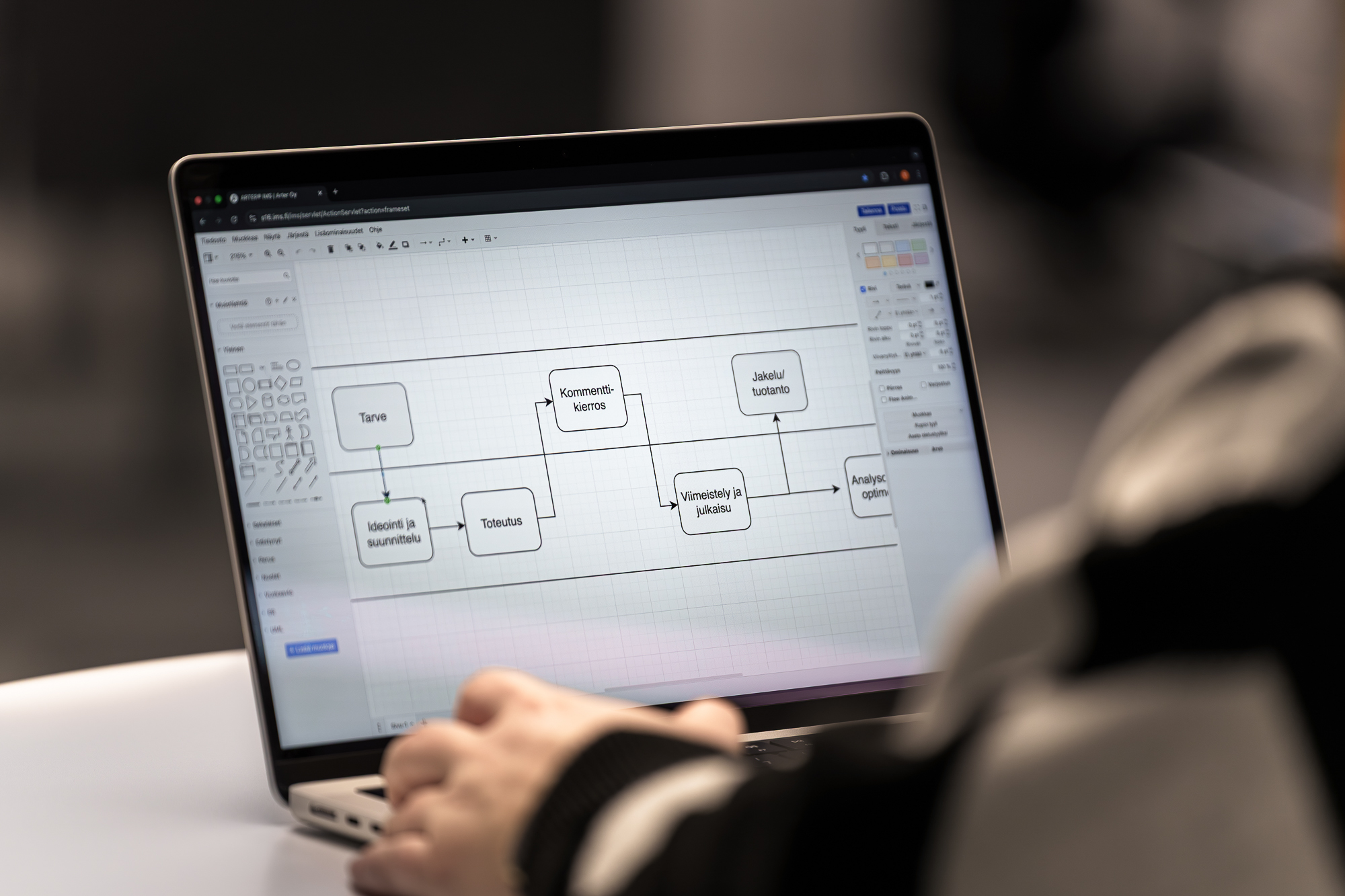
A process is:
- Process is a defined set of activities or behaviours performed by humans or machines to achieve one or more goal.
- Triggered by specific events and have one or more outcome that may result in the termination of the process or a handoff to another process.
- Composed of a collection of interrelated tasks or activities which solve a particular issue.
- End-to-end work which delivers value to customers – end-to-end involves crossing any functional boundaries.
A business process is:
- a set of activities & tasks performed by resources
- using a variety of information
- interacting in a various ways
- guided by business policies and principles
- to bring out a desired result
A business process is a collection of business activities that are comprised of a set of business tasks, that create business events, that are performed on a routine basis for a defined purpose and result.
Good processes don’t make winners, but winners make good processes.
What do process-focused organizations do?
- Place considerable focus on linking processes between individual functions for end-to-end process coverage.
- Ensure everyone is able to more efficiently utilize resources.
- Provide a common language across departments.
- Provide lessons learned supported by reliable data that can be applied to other processes and improvement activities.
- Ensure all employees understand process steps and how they add value.
- Ensure employees understand how processes are behaving.
- Ensure employees help manage each others instead of escalating conflicts.
- Hand-offs between employees are smooth and without artificial boundaries.
- Ensure processes are objectively and frequently measured and reviewed for performance fit.
- Ensure customers’ requirements are known by everyone in the organization.
- Organization structure changes from functional orientation to process orientation.
- High walls between departmental functions change to cooperative partnerships.
- Operational activities change from simple tasks to multidimensional work.
- Employee roles change being controlled to being empowered.
- Processes change from being somewhat flexibel and inefficient to being highly flexible and efficient.
- Focus on delivering value to function shifts to delivering value for the customer.
- Quality changes from being add-on to being built-in.
- Managers change from supervision to coaches.
- Processes change from being uneven to being balanced and capable.
- Focus of performance measures shifts from activity to results.
- Advancement criteria change from being performance based to being ability based.

![]() Published on:
Published on: